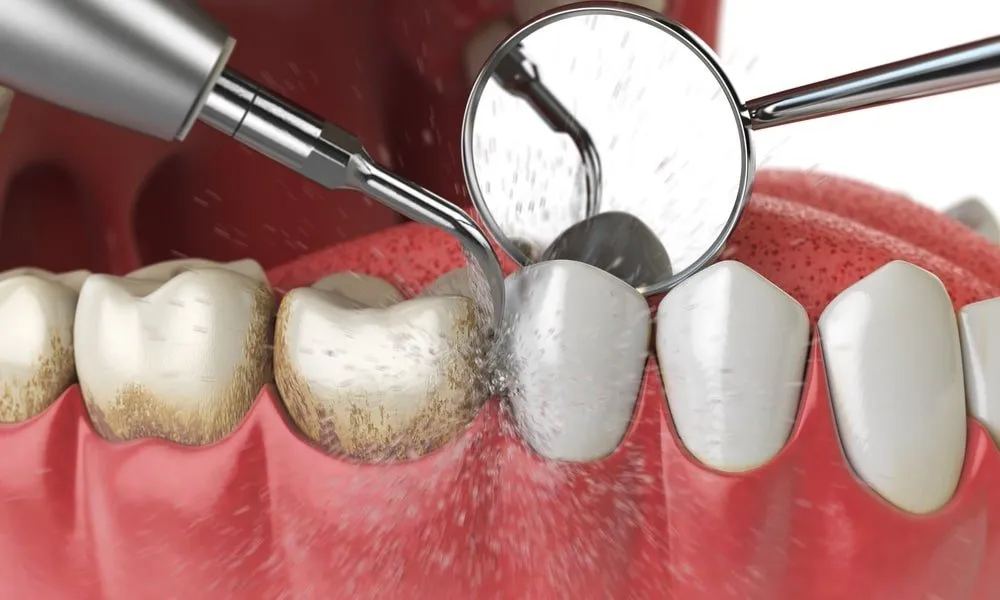
Dental plaque is a sticky, colorless film of bacteria that forms on teeth and along the gum line. It is a biofilm that develops when bacteria in the mouth attach to tooth surfaces and multiply. If not removed regularly, plaque can lead to tooth decay, gum disease, and other oral health issues. The general dentist in Chicago, IL, and their expert team offer a comprehensive approach to treating dental plaque for improved oral health. Let us explore dental plaque further.
What is dental plaque?
Dental plaque is a sticky, colorless film of bacteria that forms on teeth and along the gum line, leading to oral health issues if not removed regularly. It develops when bacteria in the mouth attach to tooth surfaces and multiply, feeding on carbohydrates and producing acid that can damage tooth enamel and cause cavities.
There are two main types of dental plaque:
- Supragingival plaque: Forms above the gum line and is visible as a white or yellowish deposit.
- Subgingival plaque: Forms below the gum line and is not visible.
How is dental plaque formed?
Dental plaque is formed through a complex process that begins with the attachment of bacteria to tooth surfaces. Initially, a protein film called pellicle forms on the teeth, providing a receptive surface for bacteria to adhere to. Oral bacteria then colonize the pellicle, feeding on carbohydrates and sugars in the mouth. As they multiply, they produce a sticky, extracellular polysaccharide matrix that traps more bacteria, creating a biofilm. This biofilm, now known as dental plaque, grows and matures, harboring a diverse community of microorganisms that can lead to tooth decay, gum disease, and other oral health issues.
What are the ill effects of dental plaque?
The negative effects of dental plaque include:
- Tooth decay: Plaque’s acid production damages tooth enamel, leading to cavities.
- Gingivitis: Plaque irritates gums, causing inflammation, redness, and bleeding.
- Periodontitis: Untreated plaque leads to infection of gums and bone, potentially causing tooth loss.
- Bad breath (halitosis): Volatile sulfur compounds produced by plaque bacteria cause unpleasant breath.
- Gum recession: Chronic plaque exposure causes gums to recede, exposing roots and increasing sensitivity.
- Bone loss: Advanced periodontitis leads to jawbone deterioration, affecting facial structure and overall health.
- Systemic infections: Bacteria from plaque can enter the bloodstream, potentially causing infections in other parts of the body.
- Heart disease: Research suggests a link between periodontal disease and increased risk of heart disease.
- Diabetes: Periodontal disease may contribute to diabetes development and worsen existing conditions.
- Tooth loss: Untreated plaque ultimately leads to tooth loss, affecting chewing, speaking, and self-confidence.
- Aesthetic issues: Plaque and tartar can discolor teeth, causing unsightly stains.
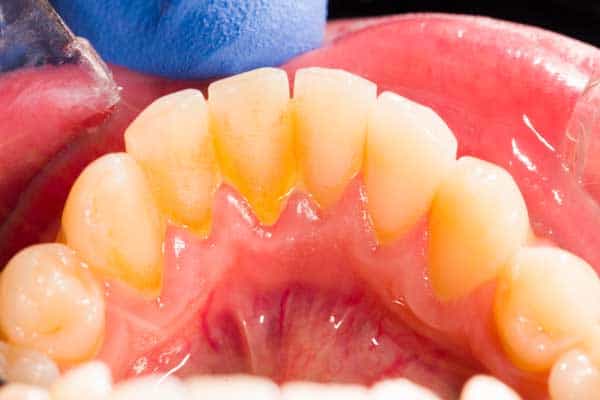
How to prevent and remove dental plaque?
Here are some ways to prevent and remove dental plaque:
Prevention:
- Brush teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to clean all surfaces of teeth.
- Pay special attention to areas where teeth and gums meet.
- Use a gentle circular motion to clean teeth.
- Floss once a day to remove plaque from between teeth and under the gum line.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash to kill bacteria.
- Limit sugary and starchy foods and drinks.
- Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.
Removal:
- Professional dental cleanings: Your dentist or hygienist will remove plaque and tartar with specialized tools.
- Scaling: A procedure to remove plaque and tartar from below the gum line.
- Root planing: Smoothing the roots of teeth to prevent further plaque buildup.
- Ultrasonic cleaning: Using high-frequency vibrations to remove plaque and tartar.
- Oral irrigation: Using a waterpik or oral irrigator to remove plaque and debris.
- Interdental brushes: Using small brushes to clean between teeth.
- Antibacterial toothpaste and mouthwash: Using products containing ingredients like triclosan or chlorhexidine to kill bacteria.
Final note
Dental plaque is a common oral health issue that can lead to serious consequences if left untreated. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental cleanings can help prevent and remove plaque, maintaining a healthy smile and overall well-being.